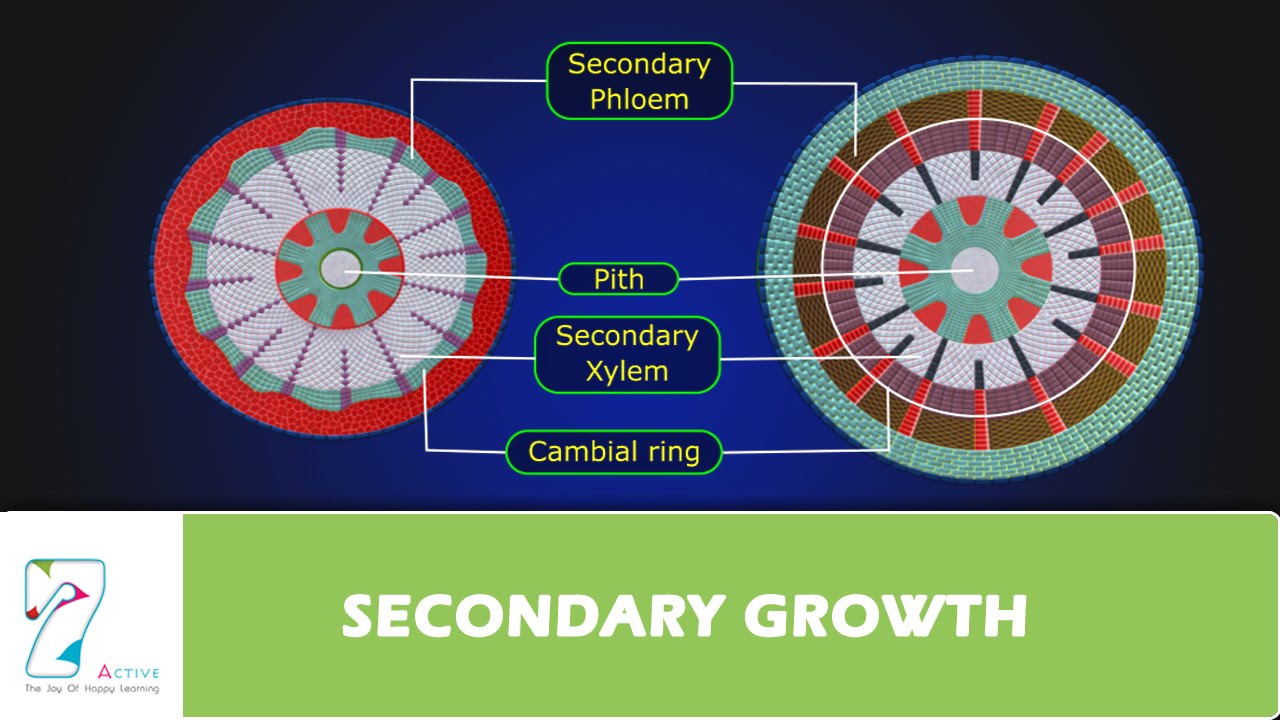
The secondary growth occurs in herbaceous and woody Lilifloarae Aloe. We will discuss only the details specific to stems.
Secondary Growth in Plants.

Plants with secondary growth. Anomalous Secondary Growth. Secondary growth or wood is noticeable in woody plants. It is abnormal type of secondary growth that occurs in some arborescent monocots eg Dracaena Yucca Agave and storage roots eg Beet Sweet Potato.
Vascular cambium Contrasted with primary growth which comes from an apical meristem. Secondary growth or wood is noticeable in woody plants. Formation of cork and formation of lenticels.
Secondary vascular tissue is added as the plant grows as well as a cork layer. This happens by the addition of vascular tissue. Conclusion Primary growth and secondary growth are the two types of mechanisms that plants use to increase the size.
Formation of secondary xylem and secondary phloem. Sansevieria Yucca Agave Dracaena and other groups of monocots. Secondary growth is absent in monocots.
Vascular cambium and cork cambium. The meristem concerned with this growth is known as cambium. It occurs in some dicots but occurs very rarely in monocots.
It is a usual feature of dicotyledonous and gymnospermous roots where it generally starts at a very early stage so much so that it is difficult to get the roots without secondary growth in most of the cases. The detailed tissue arrangement pattern after secondary growth as seen in TS. The latter forms conjunctive tissue and patches of meristematic cells.
Increases g irth of plant. Not found in all plants. One of the first groups to exhibit secondary xylem was an extinct group called the.
The cambium appears in a direct continuation of a primary thickening meristem. Herbaceous Arabidopsis plants as a model to study secondary growth The current understanding of the molecular network regulating secondary growth mainly comes from studies using the model plant Arabidopsis. Secondary growth is defined as the growth that increases the girth or diameter and thickness of the plant as a result of the activities of primary and lateral meristem ie.
T his feature is the hallmark of a true tree. There are two types of lateral tissues involved in secondary growth. While the principles are similar for secondary growth in roots the details are somewhat different.
Secondary growth or wood is noticeable in woody plants. Grasses belongs to monocots. It occurs in some dicots but occurs very rarely in monocots.
Secondary thickness takes place in three steps. The vascular cambium differentiates between the primary xylem and phloem in this zone. Plant with secondary xylem is called a lignophyte.
The lateral meristem tissues are responsible for the secondary growth of plants. The annual Arabidopsis plant undergoes secondary growth in the stem in the root and in the hypocotyl. Secondary growth in roots leads to increase in the thickness of the root.
Vascular cambium and cork cambium Cambium cells are cells that have exchange their previous. It occurs in perennial gymnosperms and dicots such as trees and shrubs. Primary and secondary growth.
The secondary growth in root also takes place by the activity of the cambium and cork cambium. Initiation of secondary growth takes place in the zone of maturation soon after the cells stop elongating there. But with the commencement of secondary growth in thickness both extrastelar and intrastelar secondary growths are seen as a result of which periderm and intrastelar secondary wood formation can be recorded.
It occurs in some dicots but occurs very rarely in monocots. The secondary growth of plants increase in stem thickness and it is due to the activity of the lateral meristems which are absent in herbs or herbaceous plants. Secondary tissues comprise the greatest volume of the root mass of woody perennial plants.
In arborescent monocot stems a secondary cambium grows in hypodermal region. Principle purpose of this lecture is to present on Secondary Growth of Plants. As mentioned earlier primary growth is the effort of the apical meristem.
The bark periderm lenticels secondary phloem and secondary xylem are developed during the secondary growth. Primary tissues continue to form in the feeder roots but the supporting root structure consists of secondary tissues produced by the lateral meristems the vascular cambium and one or more cork cambiaThe usually unobserved underground root systems of most trees are as massive as the huge aerial bodies. Secondary growth arises in regions of a woody plant where primary growth has ceased This usually occurs during the first or second year of the plants growth The process starts when differentiated cells revert to become undifferentiated cells forming 2 lateral meristems called.
Mitotic growth from a lateral meristem eg. In woody plants primary growth is followed by secondary growth which allows the plant stem to increase in thickness or girth. Herbaceous plants mostly undergo primary growth with little secondary growth or increase in thickness.
In woody plants primary growth is followed by secondary growth which allows the plant stem to increase in thickness. The details below are specific to secondary growth in stems.

Secondary Growth Of Plants Assignment Point

Figure An Overview Of Primary And Secondary Growth Of A Woody Stem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Vascular Cambium Primary P Plant Tissue Primary Growth Vascular

Plant Organs Secondary Stem Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology

Secondary Growth And Development Processes Of Plant New Science Biology

Primary And Secondary Growth In Plants Diagram Quizlet
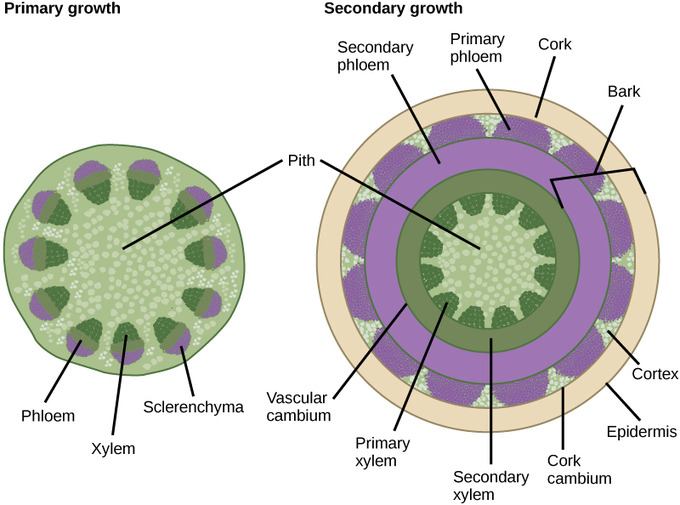
30 2c Primary And Secondary Growth In Stems Biology Libretexts
Secondary Growth In Dicot Stem

Primary Growth And Secondary Growth Shmoop Biology Primary Growth Biology Biology College

Secondary Growth As A Determinant Of Plant Shape And Form Sciencedirect

Secondary Growth In Plants Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Secondary Growth In Woody Plants Source Campbell Et Al 2000 364 Download Scientific Diagram

What Tissues Produce Secondary Growth In Plants Quora

Secondary Growth Stems And Roots Concepts Videos And Examples